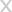Convection heaters are commonly used to provide whole-room heating. They do take a while to heat an entire room, but the warmth they produce can last long. This makes them ideal for places where people tend to stay in for long periods, like homes, offices, factories, and warehouses.
Just like any other type of heater, convection heaters have unique features that make them suitable for specific applications. In this article, we will have a closer look at what convection heaters offer, how they work, and if they are safe to use. We will also look into some pros and cons and the varieties you can choose from if you’re looking to buy a convection heater.
Convection Heater Basics
As its name reveals, a convection heater works by using convection currents. However, there are several types of convection heaters out there, and they do have some differences in terms of energy source, heating element, efficiency, and several other internal and external features. Keep reading to find out more about convection heaters.
1. How They Work
Unlike radiant heaters that use electromagnetic waves to transmit heat, convection heaters use the air itself. In a nutshell, the process involves convection currents moving throughout the heater’s body and across the heating element. The heat produced here is transmitted to the surrounding air, leading the heated air to expand and rise.
Hot air has a lower density than cool air. This is one of the most important concepts in convection heating. As heated air rises and displaces room-temperature air, the cooler air comes into contact with the convection heater and consequently gets heated up as well. The process then repeats itself: hot air rises, room-temperature air gets displaced near the device, and so on. This process repeatedly happens until you turn your device off, either manually or through an automatic shut off if your device has that feature.
Automatic convection heaters shut off once the desired room temperature has been reached. Also, some convection hears are built with a fan to speed up the process of drawing in cool air and circulating heated air.

2. Heat Sources
Convection heaters come in electric and combustion models. Electric models use electricity as the heat source, while combustion models use gas, propane, or any other type of fuel. Some models also incorporate thermal mass, such as oil heaters and night storage heaters. In terms of heating element, most models today are built with either metal coils, nickel-chromium resistance wire, thermal liquid, or ceramic.
3. Safety
It is a known fact that there have been many fire incidents that started with heaters. However, it’s important to understand that the danger is not in the heater itself but in the proximity of combustible objects to the device. Flammable objects like curtains, carpets, and combustible liquids should be as far away from a heater as possible. The general rule is that the bigger your heater is, the larger the clearance of combustible objects should be.
You should also keep in mind that some convection heaters, especially those that involve burning gas, are not ideal for prolonged use indoors. Heaters that run on gas use oxygen and produce carbon monoxide, which naturally affects indoor air quality. Worse, taking in hazardous levels of carbon monoxide can result in poisoning that can lead to dizziness, nausea, or other health issues. You can help stay safe by installing one of the best carbon monoxide detectors.
Legitimate heater manufacturers undertake quality assurance (QA) procedures before making their products available in the market. This is why it’s always best to buy heaters from reliable brands. It would also be helpful to look for safety markings indicating that a device has been tested by at least one reputable QA or certification agency. Some markings you can look for are the UL Listed, ETL Listed, CSA Approved, and Intertek Certified markings.
Once you have a reliable heater from a manufacturer you trust, you should also remember to always be mindful of safety precautions. An excellent first step is to carefully read your heater’s manual and follow important specifications like the appropriate voltage, installation, and maintenance procedures. Following these carefully and religiously go a long way to protecting you, your family or colleagues, your assets, as well as your heater.
For additional protection, some modern convection heaters come with a tilt sensor. In case your heater gets accidentally knocked off or is placed in an unstable position, this sensor automatically stops your device from working to prevent fire.
Efficiency and Energy Use
Convection heaters are the most efficient types of heaters for whole-room heating. Even though they take some time before achieving a user’s desired temperature, they do heat the air gradually, which you should be able to feel as soon as the device is turned on. This is because it is the air itself that is heated up. Other heaters like radiant or infrared heaters work differently, in that they directly heat up the objects near them. As a result, even after you turn off a convection heater, you would still be able to feel the sustained heat for a certain period of time.
Like in most appliances, the most energy-efficient electric convection heaters are often marked with ENERGY STAR®, so look for this label if you wish to get the most savings.
Do note, however, that your heater’s built-in energy-efficient components are not sufficient to lower your overall electric consumption. Remember that the higher the heater’s power rating is in watts, then the higher cost it will need to run. As such, you will have to be mindful of your heater’s power rating, how long you use your heater, and how appropriate it is for the location where you placed it.
For instance, if you need convection heaters for both prolonged indoor and outdoor use, then it might be wiser for you to have an electric convection heater for the former and a gas convection heater for the latter.
Types of Convection Heaters
There are two general classifications of convection heaters: the electric classification and the gas-fired classification. While we can also group heaters according to them being fixed (permanently installed) or non-fixed (portable), we will focus more on the previously mentioned classifications since many more types of convection heaters can be identified under them.
1. Electric Convection Heaters
Simply plug an electric convection heater to a power source, and it immediately starts running. Convenience is the primary competitive advantage of electric heaters. And if convenience is what you’re after, then you’d be glad to know that there are plenty of electric convection heaters that you can pick from.
A. Panel heaters
Panel heaters are ideal if you want to have better control of the per-room temperature of your home or office. These heaters are wall-mounted, and you can install them at any strategic part of a room as long as they are near a power socket. You can set your heaters at different temperatures per room, so you can achieve the level of warmth you want that suits your room size and the number of people who stay there.
Panel heaters are commonly used in bedrooms, living rooms, and small offices. Aside from their gradual heating capability, they are also made to provide aesthetic value. Most panel heater designs are slim, sleek, and are easy to control and program.
B. Fan heaters
Fan convector heaters are made to be either wall-mounted or freestanding. They are great choices for small rooms but aren’t so efficient for bigger rooms. Since they come with a fan, they disperse heated air more quickly. The downside, however, is that these heaters produce more noise.
C. Institutional Convector Heaters
These heaters are designed specifically for commercial and industrial spaces. Made for heavy-duty use, these heaters come with aluminum fins for a broader surface area, which then helps in heating air more quickly and distributing it evenly. These types of heaters must never be used for residential applications.
D. Hazardous Location Wall Convector Heaters
These heaters are specially designed for hazardous locations. These include gasoline stations and other spaces exposed to flammable gases, vapors, or dust particles. Different models of these heaters are made for specific classes, divisions, and groups of hazardous locations as identified and described by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). TPI Corporation, for example, has a series of hazardous location wall convection heaters that are rated for different classes, divisions, and groups.
E. Oil Heaters
Also called column heaters, oil heaters use electricity as their heat source and oil as their heat reservoir. Oil has a high heat capacity and a high boiling point, making it an effective heat pathway between the heating element and the cavities of a heater unit.
These heaters are more expensive to use than most gas-fired heaters. One of their biggest advantages, however, is their suitability for prolonged indoor use. Oil heaters don’t consume oxygen nor produce harmful gases, which is why they’re ideal for bedrooms and other small and enclosed spaces.
2. Gas-fired Convection Heaters
Just like electric heaters, gas-fired varieties also have their share of advantages that suit different situations. They are generally cheaper to buy and use than the electric types, and they’re also dependable when there's a power outage.
Aside from these, some gas-fired convection heaters are made to be suitable indoors for a certain duration of time. Just be sure to choose a heater from a reliable manufacturer and check for the manufacturer’s guide and safety reminders.
Unlike traditional heaters, the modern designs of gas-fired convection heaters are more aesthetically pleasing and space-saving. Also, fluing, which is one of the biggest problems with old gas-fired models, has already been addressed in most modern designs through flexible flue extensions or other improvements in installation.

Pros and Cons of Using Convection Heaters
Different types of convection heaters have their own pros and cons, but one general advantage that all models have is their suitability for whole-room heating. They are great choices for places wherein people tend to stay for a long time, such as living rooms, bedrooms, and even commercial and industrial spaces. Note, however, that not all convection heaters can heat up a large space.
Convection heaters warm air gradually, and it takes time for the heat to be distributed evenly throughout a room. However, you can make this process quicker by getting a convection heater with a built-in oscillating fan or use one with a separate blower fan.
As for a disadvantageous side, one recurring complaint people have about convection heaters is the noise they produce. If you want a convection heater with minimal noise, better opt for a unit that has no fans.
What do Reviews Say?
Consumer surveys support that convection heaters remain as popular heating options. Also, as expected, some of the top considerations of buyers when choosing a convection heater include the device’s energy efficiency, affordability, aesthetic quality, and convenient features like a built-in thermostat and temperature control.
Safety is also a factor that buyers consistently ask about. In fact, aside from having reliable QA marks, many buyers today prefer heaters with a programmable timer. This timer enables a heater to shut down on its own, hence preventing risks of overheating and related incidents.
When it comes to brands, some names that appear in recent surveys and reviews are Lasko, Dimplex, Stiebel Eltron, De’Longhi, and TPI. TPI is specifically known for its commercial and industrial convection heaters as well as its heater accessories that help boost the heaters’ functionality and safety features.
Convection Heaters: Yea or Nay?
The fact that convection heaters remain popular is an indication of their effective performance in providing warmth to homes and workplaces. What’s more, recent technologies have led to smaller and sleeker heater designs. These designs can blend well with any room or workspace, making them attractive choices for anyone who cares about aesthetics alongside function.
Convection heaters provide benefits that other types of heaters cannot, especially their ability to warm an entire room gradually and evenly. This kind of heating is not possible with other heating units, so convection heaters are a big yea in this aspect.
But just like any item, each buyer has personal considerations that must be taken into account. This article has provided you with plentiful information about convection heaters, and it is up to you to decide if this type of heater suits your needs.
You can find different models of convection heaters here on Engineer Warehouse. You can also find infrared heaters, forced-fan heaters, and more. Feel free to browse and weigh their features against your considerations. All heaters on Engineer Warehouse come with QA markings like Intertek’s certification and UL or ETL-Listed marks.